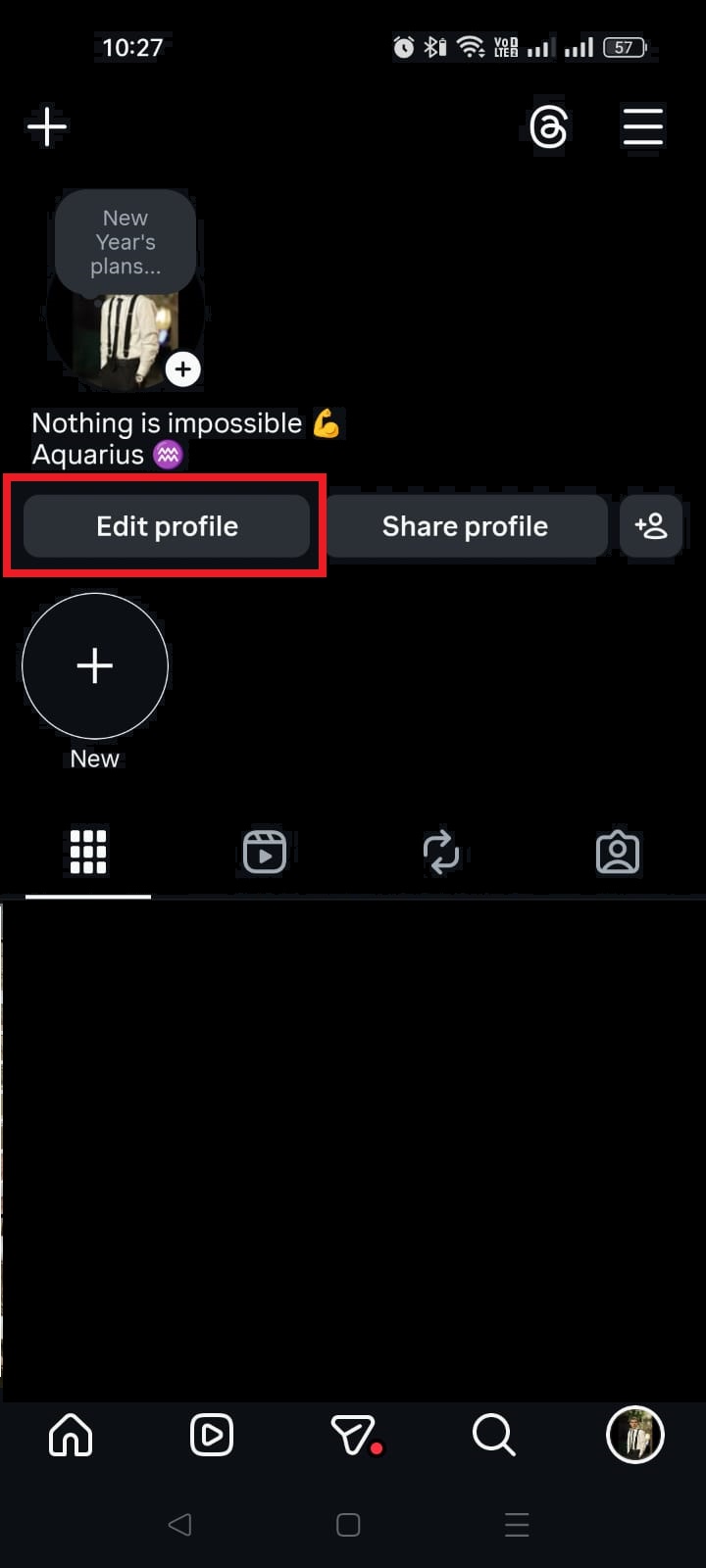
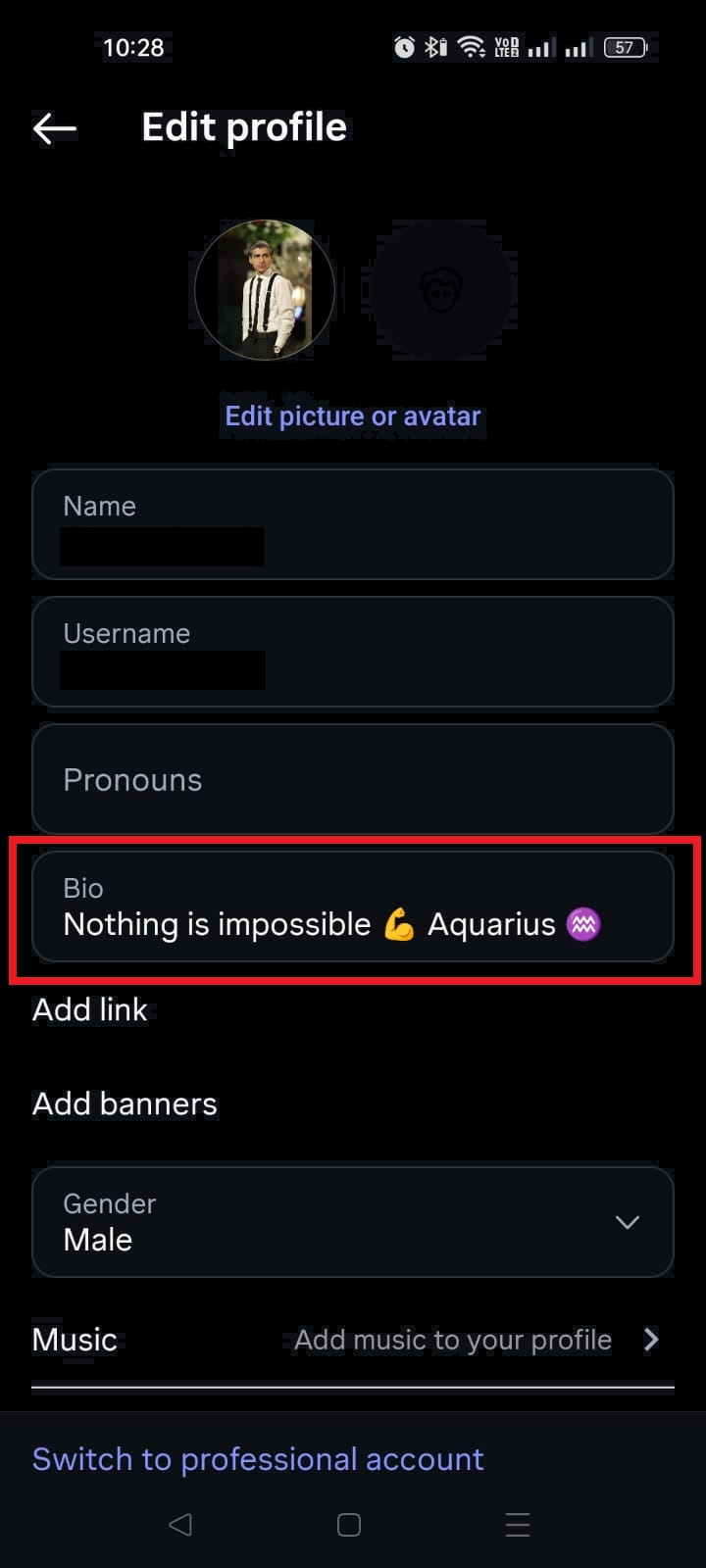
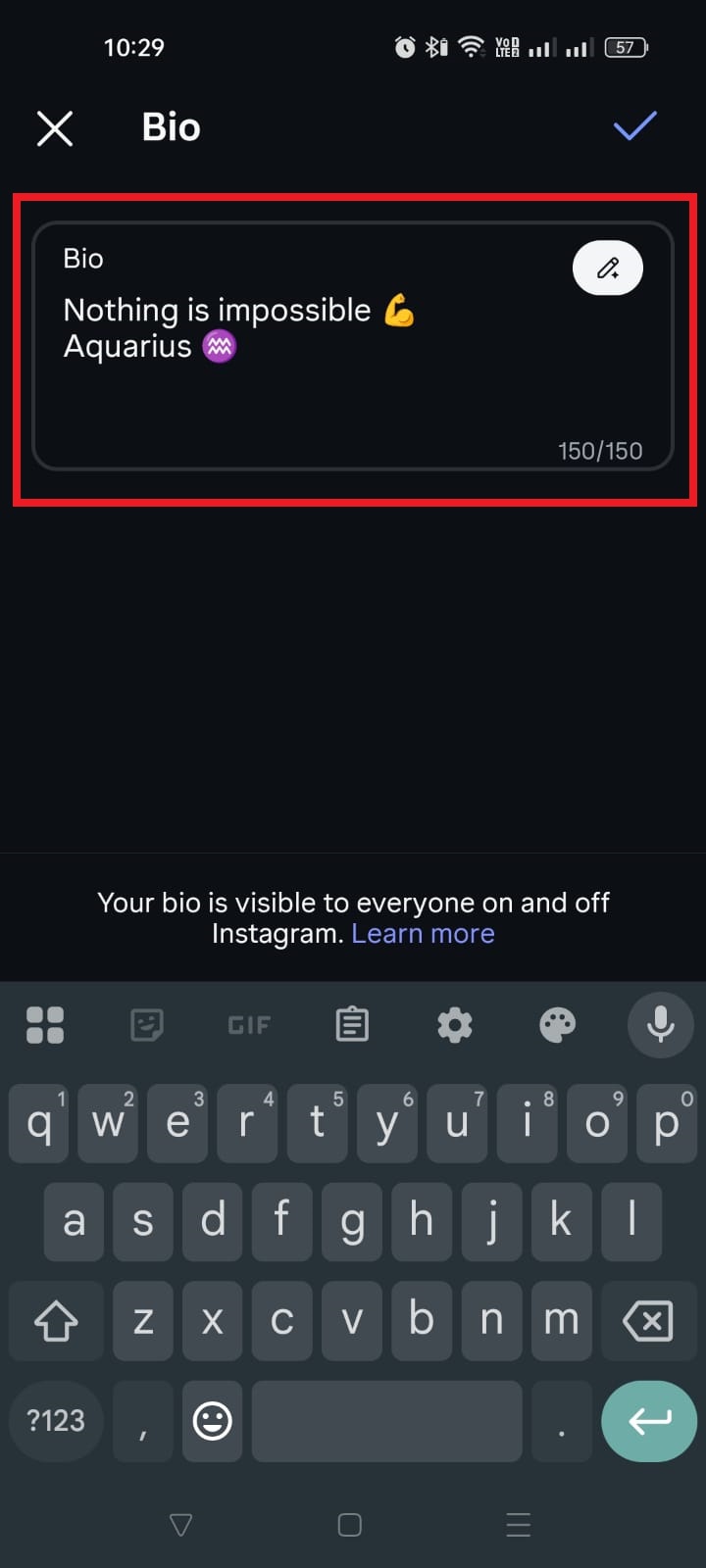
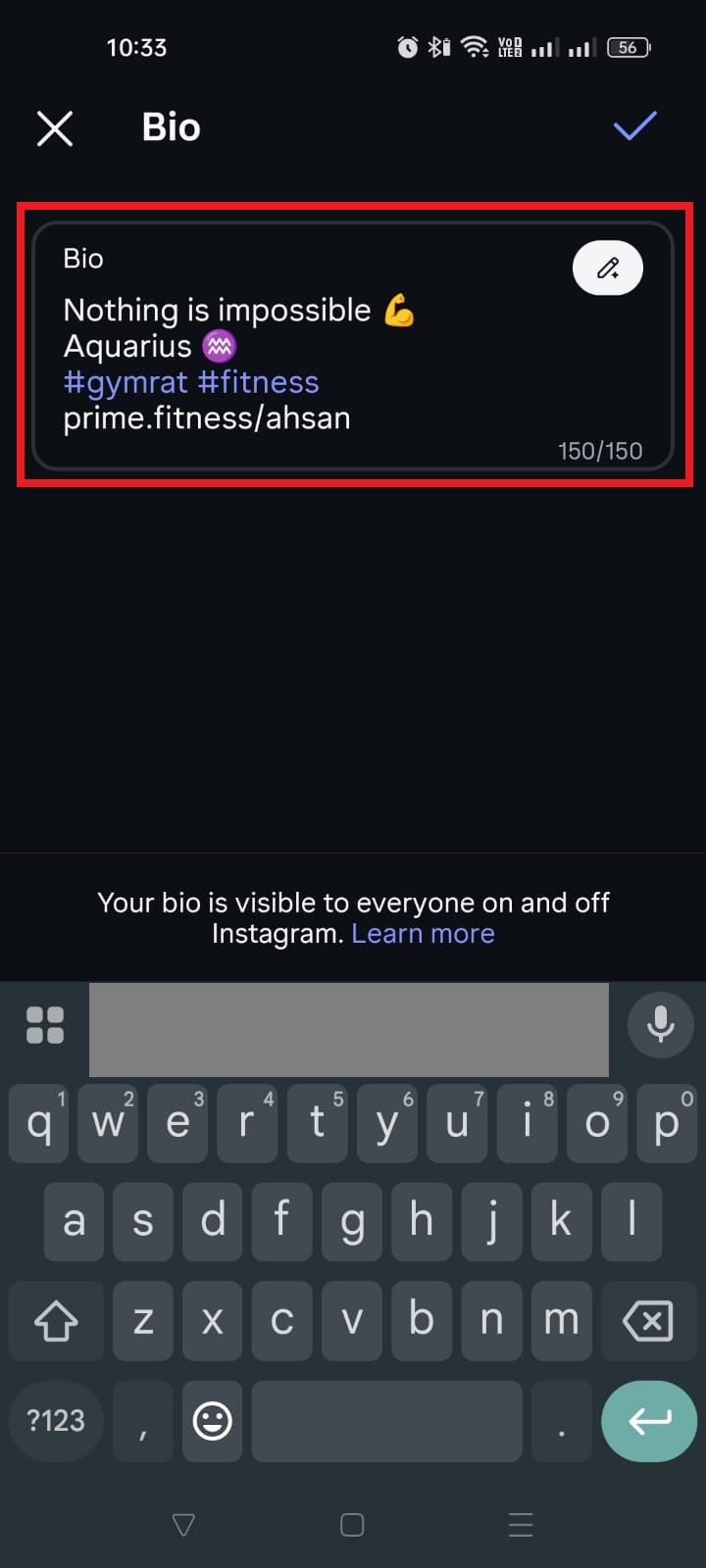
Instagram isn’t just a photo app anymore!
In 2026, it still dominates the social scene with around 2.1–3 billion monthly active users scrolling, posting, and engaging every single month.
Half a billion people use Instagram Stories daily, and Reels now account for a significant share of total engagement time on the platform.
That means if you’re an influencer, creator, small business owner, or just someone who loves sharing life’s moments, your captions matter a lot.
Great captions can boost discovery, spark conversations, and turn casual viewers into loyal followers. And let’s be honest: coming up with the perfect line can be a struggle, which is precisely why you’re here.
Ready to level up your posts?
Let’s kick things off by answering the basics…
What is an Instagram caption?
An “Instagram caption” is the short block of text you add under your photo, video, or Reel when you post it on Instagram.

It’s more than just a few words!
It’s your chance to add context, show personality, or give extra meaning that your visuals alone might not fully express.
Whether it’s a funny one-liner, a heartfelt message, or a story that pulls people in, captions help you connect with anyone scrolling through their feed.
Importance of Instagram captions: Why do they matter a lot?
Captions might seem simple, but the right words can make your post sing.
- Add context to your visuals: A caption explains what’s going on, why the moment matters, or what you want your audience to notice.
- Boost engagement: Good captions invite likes, comments, shares, and saves, all of which help your posts get seen by more people.
- Show your voice & personality: This is where you let your true self, vibe, or brand tone shine, making your content feel more human and relatable.
- Improve discoverability: Hashtags and relevant words in captions help new users find your post through search and explore.
- Encourage action: A clever CTA(“Tell me your fav emoji”, “Tag a friend”) can turn viewers into active participants.
A complete catalogue of the best Instagram captions for every mood & moment
Now that you know why captions matter, let’s get right into the fun part: actual captions you can copy and paste!

Below are top-notch lines sorted by vibe, no matter if you want something simple, trendy, or super popular in 2026 👇
Simple captions for Instagram
- Simple moments, great memories!
- Just my type of vibes ✨
- Live today, who has seen tomorrow.
- Don’t look for sunshine, be the ☀️
- Aging like a fine wine 🍷
- Breathe in the fresh air.
- Next stop, Paris 🗼
- Life paused, Monday started.
- Ready to explore new ⛰️
- Available for my people.
Trendy captions for Instagram
- Soft life, strong coffee, big dreams. ☕️✨
- Main character arc. 🎬
- Manifesting good vibes and Wi-Fi. 📶
- Today’s mood: Unbothered. 😎
- Glow up season. ✨
- POV: You just caught a vibe. 🌈
- Less scrolling, more living. 🚀
- New era. New energy. 💫
- Trending energy only. 🔥
- On everyone’s feed, still original. 🔄
Popular/famous captions for Instagram
- Less perfection, more authenticity.
- Unapologetically me.
- Just 😴 vibes.
- Catching flights, not feelings. ✈️
- In my peace era. ✌️
- Healing looks good on me.
- Coffee in one hand, confidence in the other. ☕💪
- Grind now, shine later.
- No filters. Born a 👸
- Life feels good lately. 🌟
Captions for Instagram end of year
- 2025 in memories and moments 📸
- Wrapping up with love and gratitude ❤️
- What a year it was 💥
- Ending this chapter with a smile 😊
- Lessons, laughter, and memories 🌟
- A year full of firsts and lasts 😮
- Goodbye 2025 — you were one for the books
- Closing the year with a thankful heart 🙏
- All the highs, all the feels
- Cheers to the past and what’s ahead 🥂
Captions for Instagram 2025 recap
- 2025 looked good on me 💫
- Memories made, moments lived 📘
- Lessons learned, growth earned ✨
- This year taught me so much 🔥
- Collected memories, not materialistic things 💭
- Ending 2025 with a whole heart ❤️
- From beginnings to breakthroughs
- Highlights reel ✔️
- A chapter full of joy and growth 🥰
- See you later, 2025! 👋
New year’s captions for Instagram 2026
- Hello 2026! Be kind and bright, pleaseeeeee 💫
- Ready for a brand-new start ✨
- 365 new chances start now ⏱️
- Fresh year, fresh vibes 🌺
- New year, new memories to make 🤝
- Bring on the confetti 🎊🎉
- First sunrise of 2026 🌅
- New year, same dreamer 💤
- 2026 — let’s do this! 🚀💪
- Cheers to new beginnings 🍾
Lunar New Year captions for Instagram
- Happy Lunar New Year! 🎊
- Wishing you luck, joy & prosperity 🧧
- New beginnings and good fortune ✨
- Celebrate traditions, share love ❤️
- Red, gold, and all the good vibes
- Fireworks + family + fortune 💥
- Gong xi fa cai! (Happiness & prosperity) 🐉
- May luck light your year ahead 🤲
- Lanterns, laughter & togetherness 🌃
- Let this new year be your best yet 🍀
Captions for Instagram for girls
- Confidence level: slaying every day 👑
- Sunshine mixed with a little sass ☀️
- Just a girl with big goals ✨
- Too sweet to handle, too fierce to care 👠
- Queen of my own little world 👸
- Self-love looks good on me ❤️
- Blessed, grateful, and glowing ✨
- Lipstick, confidence, and attitude 💄: Complete package!
- Keep shining, darling 🌟
- Grace in her heart and fire in her soul 🔥
Captions for Instagram for boys
- Born to stand out, not to fit in 💥
- Living life in the fast lane 🛣️
- Hustle hard, stay humble 🚀
- Just confident vibes and big goals ✨
- Nothing but good energy 🌊
- Confidence level — unfiltered 🔓
- Style on point, goals set for life 🕶️
- Creating memories that last till eternity 📸
- Stay chill, stay winning 😎
- Unapologetically me 💯
Captions for Instagram for women
- Elegance never goes out of style ✨
- A woman with a vision is unstoppable 🌟
- Strong, soft, and shining every day 💖
- Built from strength and grace 🕊️
- She’s got dreams bigger than her fears 🌈
- Amazing things happen when she smiles 😄
- Radiate kindness — it’s contagious 🦋
- Woman with ambition and a big heart 💼💕
- Wise woman, wild heart 🌙
- Queens uplift queens 👑
Captions for Instagram for men
- 100% strength with a kind heart 💪❤️
- Classic vibes, modern mind ✨
- Real men chase dreams, not followers 🎯
- Built different, determined always 💥
- Calm mind, strong actions ⚡
- Gentleman with a grind 🕴️
- Every day’s a new chapter 📖
- Living life one bold step at a time 🚶♂️
- Simple life, big goals 🌟
- Confidence in silence 🗣️🤫
Captions for Instagram couples
- Two hearts, one incredible story. 💑
- You + me = forever. ❤️
- We’re better together than Wi-Fi and memes. 📶💕
- My favorite chapter in life begins with you. 📖
- Partners in crime and in love. 😎💕
- Every day with you feels like magic. ✨
- Couldn’t imagine life without you. 🌍💞
- You’re my favorite hello and hardest goodbye. 💌
- Together is my happy place. 🏠💗
- This love feels like home. 🏡❤️
Wedding captions for Instagram
- Forever starts today! 💍
- 3rd February 2026 | Mark the date | Two hearts become one. ❤️✨
- Cheers to love, laughter, and happily ever after! 🥂
- Just married and loving it! 💑 💕
- Today, we say “I do” to forever. ✨
- With you is my favorite place to be. 🌹
- Walking into forever hand in hand. 🤝💖
- My wedding day, our perfect beginning. 📸💞
- Married my best friend — happiest day ever! 🎉 💍
- Love, joy, and a thousand memories. 🌟
Love captions for Instagram
- You’re my today and all of my tomorrows. 🌅
- Love feels better with you by my side. ❤️
- You’re the reason I believe in love. 💫
- My heart smiles every time I see you. 😊
- Life’s better when you look at me with a smily face. 💕
- You make love look easy. 💖
- Every moment with you is a blessing. 🌟
- I love you more every single day. 💞
- You are the sunshine in my life. ☀️ ❤️
- Love is our greatest adventure. 🌍 💖
Self-love captions for Instagram
- I am enough, just as I am. 🌟
- Learning to love myself more each day. 🌱
- Self-love isn’t selfish; it’s essential. 💖
- Growth starts with self-kindness. 💛
- My journey, my joy, my growth. ✨
- I choose me — every single day. 💕
- Embracing imperfections with pride. 🌿
- Loving myself is my first love story. 💫
- Confidence looks good on me. 💃🏻💖
- Today, I celebrate myself. 🎉💗
Relationship captions for Instagram
- Every classic love story is my favorite — ours especially 🌟
- You’re my favorite, somewhere between ‘hello’ and ‘forever.’ 🌙
- Love planted a rose, and the world turned sweet 🌹
- We’re better together than we ever imagined 💞
- Two hearts that beat as one ❤️
- You make every day feel like something special ✨
- Together isn’t just a place — it’s the most beautiful feeling 💘
- Loving you is my favorite adventure 💫
- Found the one I never want to let go 🤝
- My partner in love and life 🥰
Romantic captions for Instagram
- I say it openly, you’re the love of my life 🌅
- Every moment with you feels special 💫
- I fell for you in the best way possible 🥂
- You’re the smile behind my everyday 😊
- Love is simple — it’s just you and me ❤️
- I never knew love until I met you 💗
- You’re my favorite chapter in my life’s book 📖
- Catching feelings and holding them tight 💕
- With you, love feels effortless 💞
- My heart beats in your rhythm 🎶
Valentine’s Day captions for Instagram
- You’re my favorite love story 📚
- Love isn’t perfect, but it’s ours 💕
- Happy Valentine’s Day to my forever person 🌹
- You + me = the perfect combo 💖
- Today, tomorrow, always you 🌟
- My heart is yours — Valentine’s & every day 💓
- Be mine forever and always ✨
- You’re my favorite notification 😉
- This Valentine’s Day, it’s still us 💗
- Love is sweeter with you, my love 🍫 ❤️
Moving on captions for Instagram
- Goodbye is the start of something better 🌱
- I choose growth over pain ✨
- Healing isn’t optional — it’s beautiful 🌸
- Better days are on the horizon ☀️
- New beginnings, new me 🌈
- I release what no longer serves me 🕊️
- Forward only, no looking back ➡️
- I’m focusing on my own happiness 🌟
- Lessons learned, strength earned 💪
- Life’s too short — I’m choosing peace ☮️
Attitude captions for Instagram
- I don’t follow the crowd — I create my own path. 😌
- Unapologetically me, always. 💥
- Too rare to care. 🌟
- I walk with purpose, talk with conviction. 🛣️
- My vibe is my signature. ✨
- Boss energy, every day. 👑
- I possess a built-in quality to turn my pain into power. 🚀
- My confidence speaks louder than words. 🔊
- I don’t need validation — I have myself. 🔐
- Built this energy myself. 💪
Confidence captions for Instagram
- Confidence is my daily armor. 🛡️
- My self-worth is my superpower. 🌟
- I’m not seeking approval — I’m living my truth. 🙌
- Faith ain’t loud — it’s a silent strength. 🤫
- I shine brightest when I believe in myself. ✨
- My vibe attracts my tribe. 💫
- Confidence looks good on me. 💁♀️
- Own who you are — no apologies. 💯
- My standards stay high, just like my goals. 🎯
- I trust myself more than empty words. 🤝
Motivational captions for Instagram
- Nothing is impossible 🏆
- Dream big. Work hard. Stay focused. 🚀
- Hustle in silence, let success make the noise. 🔥
- Don’t wait for opportunity — create it. 💼
- Push yourself, coz no one else will. 💪
- Your only competition is yesterday’s you. 📈
- Every step forward counts. 👣
- The harder you work, the greater you’ll feel. 🏆
- Believe you can — and you’re halfway there. ✨
- Success isn’t a destination — it’s consistency. 🔄
Inspirational captions for Instagram
- Be yourself; everyone else is already taken. 🌈
- Stars can’t shine without darkness. ✨🖤
- Let your attitude be as bright as your future. 🌞
- Believe in yourself, and you’ll be unstoppable. 🚀
- Be the energy you want to attract. ⚡
- Turn your setbacks into comebacks. 🔥
- Remember, your story motivates someone, somewhere. 🌍
- Kindness costs nothing, but changes everything. 💖
- Small acts of love create massive ripples. 💕
- A positive mindset creates a positive life. 💫
Sports captions for Instagram
- Game face on, nothing can stop me. ⚽🔥
- Chasing dreams one game at a time. 🏃♂️✨
- Victory tastes sweeter after struggles. 🏆
- Sport is life — everything else is pause. 🎮
- Fast feet, fierce heart, endless hustle. 💨
- Stay focused, play harder. 💪
- Every sweat tells a story. 🏅
- Teamwork makes the dream work. 🤝
- Fuel your passion, chase your dreams. 🏃♀️
- Play hard like it’s your final game. 💥
Fitness captions for Instagram
- Gym is not a destination — it’s a way of life. 🏋️♀️
- Sweat now, shine later. 💦
- Stronger every day, one rep at a time. 💪
- Push harder today, be stronger tomorrow. 🔥
- Train hard, stay humble. 🏆
- Your body can stand almost anything — it’s your mind you have to convince. 🧠
- Fitness first, excuses last. 💯
- Sweat, work hard, repeat. 🏆🎯💎
- No pain, no gain. 🚀
- Find your strength, unleash your power. 🔥
Classy captions for Instagram
- The one with sheer class never compromises. 😎
- Elegance is my superpower. 💫
- Keep it graceful, always. 💎
- In a world full of trends, remain classic. 🕊️
- Dress how you want to be addressed. 👗
- Elegance never goes unnoticed. 🌟
- Charm is my secret accessory. 💖
- Radiate class, captivate hearts. 💛
- Stay polished, poised, and confident. ✨
- Less drama, more elegance and class. 🌹
Sassy captions for Instagram
- Too glam to give a damn. 💅
- Confidence level: Selfie with no filter. 😎
- I’m not bossy — I’m the boss. 👑
- Caution: I know my real worth. ⚠️
- Not your speed, so stay in your lane. 🛣️
- I don’t chase, I attract. 🌌
- Main character energy. 🎬
- Warning 🚨: I may be too hot to handle. 🔥
- Born to stand out — fitting in was never an option. 🌟
- Sassy but always classy. 👸🏻👠
Swaggy captions for Instagram
- Too rare to be compared 💎
- Love me or hate me — either way, I win 😏
- Walking like a masterpiece, talking like a boss 🎭
- My vibe, my rules, no exceptions ⚡
- No GPS needed — I make my own way 🛤️
- I’m a limited edition, not a copy-paste product 💽
- Hustle hard, talk less 🎯
- I don’t follow trends, I set them one at a time 🕶
- Not everyone deserves my energy 🔥
- My success is my revenge. 😈
Savage captions for Instagram
- Be savage, not average 💯
- Catch flights, not feelings ✈️
- Mess with me? I dare you 😏
- I’m the truth — face it 👑
- No time for fake friends 💔
- Too busy being a legend 🌟
- Your opinion? Never heard of it 😘
- Built different 💪; Ain’t my fault!
- Born to slay, not just play 🔥
- Silent moves, bang in results 🌙
Captions for Instagram for baddies
- Filters? Never heard of her. 📸
- My face is an ugly vibe. 🤡
- Cute face, killer mindset. 💥
- Barbie vibes, Oppenheimer mind. 🧠
- Looks like a snack, thinks like a CEO. 💼
- Soft girl, but by face, not by heart. 🔪
- Mirror: exists — Me: works it. 💁♀️
- I’m not photogenic — I just look good. 😎
- Say hi to your new obsession. 🍷
- Classy with a savage twist. Don’t come close 💣
Cute captions for Instagram
- Sweet smiles & sunshine vibes 🌞
- Cuteness overloaded — handle with care 💗
- Little moments, big smiles 😊
- Smiling because life’s too short not to 🌸
- More giggles, fewer worries ✨
- Small happiness, big heart 💕
- Soft heart, chill vibe 🌿
- Too adorable to handle 😍
- Bliss looks good on me ✨
- Smiling into the weekend 😄
Funny captions for Instagram
- Life’s too short to take seriously — just laugh and move on. 😄
- I’m on a seafood diet — I see food, I eat it. 🍔
- My bed is a magical place where I remember nothing. 🛏️
- I’m not clumsy; the floor just hates me. 😅
- Reality called — I hung up. 📞😂
- Plot twist: I’m a hilarious circus joker. 🤡
- Running late is my cardio. 🏃♀️⏰
- Life gives lemons… I make funny faces. 🍋😜
- My favorite hobby? Laughing & overreacting, ahem ahem 😉
- I have a problem for every solution 😆
Witty captions for Instagram
- Life is short — smile while you still have teeth. 😁
- I put the “pro” in procrastinate. 🕖
- I’m not weird — I’m limited edition. ✨
- I’m an acquired taste — if you don’t like me, acquire some taste. 😏
- I’m not lazy — energy-saving mode activated. 🔋 😌
- I’m not short — I’m concentrated awesome. 🔥
- I’m not perfect, but my eyebrows are. 😉
- My life feels like a test I didn’t study for. 📚
- I’m not ignoring you — I’m prioritizing my naps. 😴
- I’m not sarcastic — I’m just fluent in words. 🤨
Clever captions for Instagram
- When nothing goes right… Go left. ⬅️
- I followed my heart… it led to the fridge. 🍕 ❤️
- Normal is boring — I prefer dramatic. 💃 😉
- Some beautiful paths can’t be discovered without getting lost. 🍂
- My vibe? Sparkly chaos with a hint of coffee. ✨☕
- I’m not short — I’m just more fun per inch. 🥳
- If awkward were a sport, I’d win gold. 🥇
- Don’t be afraid of your shadow; it reminds you there’s light 🕯️
- I’m not procrastinating — I’m creatively thinking. 🤔
- Not everyone likes me, but not everyone matters. 🔥
Chill captions for Instagram
- Just vibing with the universe. 🌌✨
- No rush, just smooth flow. 🌊
- Breathe in good vibes, exhale the rest. 💨
- Peace looks good on me. 🌼
- Sunday should come with a pause button. ⏸️
- Lost in the moment, found in the stillness. 🌾
- Stay low-key — not everything needs the limelight. 🤫
- Mondays are for sunsets and self-care, not office work 🌅
- Let’s wander where Wi-Fi is weak. 🌲
- Just a chill day with only +ve vibes. ✌️
Catchy captions for Instagram
- Catch me if you can, not my feelings. 🙏
- Try not to follow the crowd — lead it. 🚀
- Make your life your biggest story. 📖 ✨
- Sparkle a little — you’re worth it. 💎 ✨
- Don’t wait — create your moment, NOW! 🎬
- Stay tuned — life’s getting better. 📺 🌟
- Good vibes, great days, the best life. 🌞 💛
- Trendsetter 💥, not a trend follower like you.
- Life’s too short for boring captions. 😉
- Scroll-stopping moments start here. 📸 🔥
Happy captions for Instagram
- Today’s a good day to have a good day 🌟
- Smile big, laugh often 😁
- Let your smile be your signature accessory 😊
- Surround yourself with things that make you smile 🌼
- Choose joy, spread love ❤️
- Happiness looks good on you ✨
- Sunshine and smiles all day ☀️
- Living life on the bright side 🌈
- Today feels like pure happiness 💛
- Catching joy at every turn 🌻
Positive captions for Instagram
- Positive vibes only — watch how life unfolds 🌟
- Life shines brighter when you focus on the good ☀️
- Sunshine state of mind, even on cloudy days 🌞
- Every day is a fresh start for good energy 💛
- Filling my heart with gratitude and joy 💖
- Optimism is my superpower 🌈
- Finding beauty in every moment 🌸
- Choose happiness and shine like a 💎
- Little happy moments in life reflect big positivity 💫
- Bright minds possess bright life 💡
Sad captions for Instagram
- Sometimes the smile we wear is the heaviest burden 😞
- Silence speaks when words can’t 😭💔
- Lost in my own thoughts and feelings 🌪😶
- Heavy hearts like heavy clouds need a little rain ⛈💧
- My silence is another word for pain 🤐💔
- Behind every fake smile, there’s a story 😔
- Broken but still standing 💔
- Tears speak louder than words 😢
- Wandering in the shadows of thoughts 🌑
- Trying to hold it together 💔
Bad days captions for Instagram
- Not every day is a good one 😞
- Feeling off today, but I’ll be okay 🙄
- Sometimes it’s okay not to be okay 💔
- Off days happen — I’m riding this wave 🌧️
- Low energy, heavy thoughts + heart 😔💔
- Bad days build better you for future 🌧️🌞
- Today’s mood: Don’t text me 💬
- Still smiling through the storm 😉, that’s me!
- Learning from the low days 📘📝
- Even cloudy days have their lessons ☁️
Deep captions for Instagram
- Sometimes silence weighs more than words 🤫
- Depth of feelings can’t be measured on a scale 📏❣️
- Stars can’t shine without a bit of darkness 🌟🌑
- My smile hides an ocean of untold stories 😊🌊
- Echoes of laughter now whispers of the past 💔🔊
- Sometimes you swim through the dark to reach the light 🏊♀️🌘
- A mind heavy with unspoken words 🏋️🤐
- Depth is knowing when to let go 🌊 ✨
- Echoing emptiness in a room full of memories 🖖👻
- Backstory over highlight reel 🧠📖
Petty captions for Instagram
- Nominal, but make it peaceful. 🤍🕊️
- Smiling through the shades. 🕶️
- My peace costs more than your drama. 💰
- Too fabulous to hide. 🤩
- Petty vibes, classy life. 🤵
- Cheers to all the wonderful moments. 🥂
- Leveling up with humor only. 🚀
- Unpopular but unstoppable. 💪
- Attitude painted red. 🩸
- Sipping on my own vibes. 🍹
Aesthetic captions for Instagram
- Lost in the beauty of the moment. ⛅️🏞️
- Chasing sunsets and dreams. 🌅💭
- Creating my own sunshine. 🌞💕
- Finding peace in the chaos. ✌️🕊️
- Radiating electrifying vibes only. ⚡🔥
- Simply stunning in simplicity. 💎🌟
- Wherever life plants you, bloom with grace. 🎗️🦋
- Let the magic unfold; just look at the night sky. 🔮🌌
- Capturing the quiet, unique moments. 🌻📸
- Elegance in every breath and step I take. 💃✨
One-word captions for Instagram
- Ethereal
- Serene
- Wanderlust
- Radiant
- Fierce
- Bliss
- Mystique
- Unbothered
- Unstoppable
- Chic
Four-word captions for Instagram
- Believe → Achieve → Repeat → Succeed. 🔥💯
- Stay focused, stay winning. 💪🏅
- Made for the spotlight. 😎
- Remember, nothing is impossible. 🤝
- Calm waves, clear mind. 🤍
- Sunsets and city lights. 🌆
- Lost in wild thoughts. 🙃
- Coffee, clouds, cozy mornings. ☕☁️
- Always hit the target. 🎯
- Get now → one left. 😏
Birthday captions for Instagram
- Birthday glow activated. ✨🎈
- Cake calories don’t count today. 🍰💁♀️
- Too blessed to stress this year. 🙏✨
- Leveling up in style. Finally, I’m 25! 🚀🎂
- Today I celebrate myself. 🎉💛
- Cheers to another year of laughter and love. 🥂❤️
- Birthday mood: sparkling and unstoppable. 💎🎈
- Blessed with another year of adventures. ✨🌍
- Cake, candles, and chaos—it’s my day! 🎂🎊
- Another trip around the sun = infinite memories ahead. ☀️🎉
Travel captions for Instagram
- Adventure awaits just outside your comfort zone. 🌄
- Let’s find a beautiful place to get lost together. 🏞️
- Passport stamps and memories that last a lifetime. 📍✈️
- Lost in wanderland. 🌿✈️
- Wanderlust in my veins from day one. 🌍💫
- Life is short, and the world is wide. Let’s explore it! 🌐
- Collect moments, not just things. 📸💭
- Travel far, dream deeper. 🌏✈️
- My type of vibe. Chasing horizons and sea breezes. 🌅🏖️
- The road is there—Don’t think, just take it. 🚗🌄
Song lyrics/music captions for Instagram
- Tonight’s gonna be a good night. 🥳
- We found love in a hopeless place. ❤️🔥
- Shine bright like a diamond. 💎
- I don’t wanna stop the music. 🎶
- If the world was ending, I’d wanna be next to you. 👩🏻❤️👨🏻
- Turn the lights down low. ✨
- Raise your glass to the sky. 🥂
- Say my name and everything just stops… 🌙
- It’s the beat my heart skips when I’m with you. 🎀
- This moment, we own it. 🔥
Food captions for Instagram
- Good food, good mood. 🍕🍔
- Food is my love language. ❤️🍽️
- Eating my way through life, one bite at a time. 🍴🌍
- Life is too short for vegetables. 😋
- Food coma, here I come. 💤🍟
- Brunch, lunch, and everything in between. 🥞🍱
- Savoring the flavor of the moment. 🍽️✨
- Taste the world on a plate. 🌍🍴
- First we eat, then we do everything else. 😄 🍽️
- Food is the ingredient that binds us all together. 🍲🤝
Captions for Instagram for selfies
- But first, let me take a selfie. 😎
- I woke up like this, still shining, huh! ✨
- Coffee and confidence, in a single snap ☕💁♀️
- Smile big, laugh often. You only live once! 😄
- My camera, my selfie. 📸
- Feeling cute, might delete later. 😜
- Glow on; the world is watching. ✨
- Mirror check. ✅ 💫
- Selfie mood: 100% 🔥
- Perfectly imperfect. 💖
Self captions for Instagram
- Me, myself & 2026 ✨
- Glow from within 🌟
- Solo vibes, big dreams 🚀
- Inner peace > outer chaos 🕊️
- My story, my rules 📖
- Self-love is power 💎
- Evolving daily 🌸
- Confidence unlocked 👑
- Just vibing in solitude 🌈
- Becoming my best version, slowly and gradually 💯
Nature captions for Instagram
- Nature never goes out of style. 🌿
- Sky above, earth below, peace within. 🌌
- Take only memories, leave only footprints. 👣
- Lost in the beauty of the outdoors. 🌲
- Mother Nature’s masterpiece. 🎨
- Fresh air, clear mind. 🍃
- Ocean air, salty hair. 🌊
- Let nature be your guide. 🌾
- Life feels better closer to Earth. 🌍
- Wild and free under open skies. 🕊️
Engaging captions for Instagram
- What’s the best thing that happened today? 💭
- If you love me, caption this for me! ✍️
- Double-tap if you can relate 🙌
- Tell me your vibe in one emoji ✨
- Best comment gets a shout-out! 🔥
- Guess where this was taken? 📍
- Swipe right to see the magic ➡️
- Tag someone who needs to see this 👀
- Your turn: drop your dream travel spot ✈️
- If you could describe today in one word, what’d it be? 💬
Cool captions for Instagram
- Get in my circle. Cool vibes only. 😎
- Life’s too short to be anything but cool. ❄️
- Stay cool, calm, and collected. 🧊
- Cooler than the flip side of the pillow. 🛏️
- Just another day being effortlessly cool. 🌤️
- Sunglasses on, cool mode activated. 🕶️
- Ice-cold confidence in a warm world. 🔥
- Cool kids never go out of style. ✨
- Living life with an extra dash of cool. 🌟
- Coolness is a state of mind, and I own it 👑
Punchy captions for Instagram
- Life is short. Skip to the punchline. 🎤
- Just me. What about you? 🤳
- Sunshine in my pockets. ☀️
- Be a mirror, not an echo.
- Dreaming of 🍕, eating a 🥗
- Selfie queen by choice. 👑
- Keep calm and like this post. 👍
- I’m in a long-distance relationship with nature. 🌲
- Tiny girl, giant adventures. 🏕️
- Climbing mountains, but not for the views. 🏔️
Unique captions for Instagram
- Overflowing with moonlight and sparkles. 🌙✨
- Pure magic in every little detail of hers.🧙🏻♀️
- Collecting memories, not just 🖼️
- Here’s a 🎁 wrapped in kindness and cozy moments. 🥰
- Live your life as you own it. 💯💪
- Smiling my way into 2️⃣0️⃣2️⃣6️⃣
- A heart full of golden dreams. 💛
- Floating through life with grace. 🦋🕊️
- Sweet like honey, bright like 7:00 am sunshine. 🍯
- Little joys make the biggest stories. 📜
Stylish captions for Instagram
- Sleek and unstoppable lady at the 🚪. Open, please. 💃
- Searching for charm in every moment. 😉
- Fashionably fearless. 😤🔥
- My confidence is the best accessory I have. 💯
- Trends fade, style stays. 🌟
- Dress like the world is watching. ⚡
- Who’s always on point? Yes, it’s me! 😉
- Don’t follow the trend; be one yourself. 😎
- Own the runway—wherever you go. 🛣️
- Finding the definition of ultimate style: Just look at my Insta handle! 👑
Smile captions for Instagram
- Smile mode activated on 1st January 2026 😄
- My smile has its own fan club. 💕
- Smiling like life is a celebration. 🌸
- Your smile is the best kind of magic I’ve seen in life. ✨
- Smile like you own the world. 🌍
- Happiness begins with a simple smile. 😃
- Sweet smiles and brighter days ahead. 🍬
- Your smile—my sunshine. ☀️
- Smile at my face because today feels right. 😊
- A genuine smile is the world’s best armor. 💥
Emoji captions for Instagram
- 🌟✨❤️
- ☀️🌈🎉
- 🌸😊💫
- 😎🔥💥
- 🌙🌊✨
- 🍕😋❤️
- 📸💛🌟
- 🎶🎧🕺
- 🐾🐶💞
- 🍰🥂🎈
Sweet captions for Instagram
- Sweet smile, wild mind. 😈💋
- Simple joys, big smiles. 🌼😊
- My own sunlight, no filter. ☀️💖
- Sweet moments make the best memories. 📸💕
- Cozy vibes and clean energy. ⚡🔋
- Sweetheart, bright soul. 💗🌟
- Just warm hugs and soft smiles. 🤗🌸
- Living life in calm colors. 🎨💕
- Just another perfect day. 💫☀️
- My comfort zone looks cute. 🏡💖
Dress captions for Instagram
- Dressed to the nines. 💃
- Classic beauty, modern mood. ✨
- Flowy, fab, and feeling free. 🌸
- Dress like you own the world. 🌎
- Maxi dress magic. 🌙
- Mini dress, major style. 👗
- Elegance wrapped in every thread. 💫
- Tonight’s outfit has a story. 📖
- Threads that tell tales. ✨
- Slaying softly in silk. 🌟
Make up captions for Instagram
- Life may not be perfect, but the makeup can be! 💄
- Winged eyeliner so sharp, it could cut one in half! 😼
- Brow game strong, confidence stronger. 💁♀️
- Lipstick can’t fix everything—but it’s a starting point, for sure! 💋
- Highlight gleam, world dream. 🌟
- Contour on point, vibes on fire. 🔥
- Beauty in progress, one brush at a time. 🖌️
- When in doubt, wing it out! ⚡
- Makeup is art; my face is the canvas. 🎨
- Sparkle today, slay tomorrow. ✨
Beauty captions for Instagram
- Be your own kind of beautiful. 💕
- A sweet smile is the cutest thing you can wear. 👑
- Glow from within and let it shine. ✨
- Beauty begins the moment you decide to be yourself. 🌸
- Radiate positivity—that’s real beauty. ☀️
- Real beauty needs no filter. 💎
- Inner beauty is the best kind of grace. ❤️
- Your +ve energy is your prettiest feature. 💫
- Some angels don’t have wings. I mean, just look at you. 😇
- Every angle tells a beautiful story. 📸
Pretty girl captions for Instagram
- Just another beauty queen in the wild. 👑
- Glitter in my veins and stars in my eyes. 🤩
- Pretty vibes, pretty life. 🌸
- Glamour with a side of grace. 💖
- Never seen a star so bright and beautiful. 🌟
- Cute today, cuter tomorrow. 💕
- Girl power and good vibes only. 🔥
- My kind of magic—self-made. ✨
- Fashionably late but always cute. 👠
- Beauty with brains and attitude. 💁♀️
Flower captions for Instagram
- Petals and power poses. 🌸
- Bloom where you’re planted. 🌼
- Flowers make everything even prettier. 🌷
- Blossoming in style. 💐
- Nature’s art worn with grace. 🌿
- Sunshine, petal prints, and smiles. ☀️🌸
- A walking garden of dreams. 💫
- Soft blooms, strong roots. 🌱
- Life is short—wear flowers. That suits you! 🌺
- Floral heart, blooming soul. 💖
Minimalist captions for Instagram
- Silence speaks. 🗣️
- Just here. 👇
- Pure & simple. 🤍
- Less talk, more work. 💻
- Peace in pixels. ₊ ⊹
- True vibes only. 🙏
- Living calm moments. 🤲
- Soft inside, strong outside. 💪
- Humbleness always wins. 💯
- Available for loved ones 24/7! 🕛
Graduation captions for Instagram
- The tassel was worth the hassle. 🎓
- And so the new adventure begins. ✨
- Caps off to new beginnings. 🎩
- Next stop: masters in motion. 🚀
- Diploma in hand, future in heart. 💖
- From books to big moves. 📚➡️💼
- May your cap fly as high as your dreams. 🌟
- This moment was earned with 100% dedication. 🏆
- Cheers to journeys ahead! 🥂
- Officially chapter two. 📖
Prom captions for Instagram
- Surely a night to remember. ✨
- Prom vibes: sparkle & shine. 💫
- Dressed to impress. 👗
- Dancing through dreams. 💃
- Prom night magic. 🎉
- Tonight we shine brighter. 💎
- Memories in the making. 📸
- Suit up & show up. 🤵
- Glitter, glam, and good times. ✨
- A memory worth a thousand snaps. 📷
Playful captions for Instagram
- Smiling like it’s my superpower. 🔋
- Too playful to pause. ⏸️
- Catch flights & silly vibes. 🤪
- Life’s better when you play 🏀.
- Side effects of 🎲: laughter + joy.
- Playful heart, carefree soul. 🥰
- Just here for the giggles. 🤭
- Whimsy mode: 🔛
- Too fun and fabulous! Be aware! 😎
- Light heart, bright day. 🌞
Bike captions for Instagram
- Two wheels, endless vibes. 🚴
- Ride at your own pace. 🔥
- Freedom on two wheels. 🙌
- Pedal, breathe, repeat. 🚴♀️
- Life feels lighter on a bike ride at night. 💥
- Road + Rhythm = Endless joy. 👌
- Wind in hair, road ahead. 💨
- Every ride has a hidden story. 💔
- Wheels turning towards ⛰️, heart smiling at its peak!
- Adventures start when the tires roll. ☸
Car captions for Instagram
- Life’s a highway—let’s take on the ride. 🚘
- Full tank, full heart. ❤️
- Windows down, music up. 🎶
- Ride it like you stole it. 🚗💨
- Cruisin’ into memories. 🌅
- Road therapy: engaged. 🛣️
- My sports car is my happy place. 🏁
- Going wherever the road leads. 🏞
- Petrol in the tank, freedom in the soul. 🔥
- Sunsets look better from the driver’s seat. 🌇
Book captions for Instagram
- Lost between the pages. 📖
- Reading is my ultimate escape. ✨
- Books & coffee = perfect combo. ☕📚
- Just one more chapter… 😅
- Stories that stay with you in good & bad times. ❤️
- Where words become worlds. 🌍
- My weekend is booked. 😌
- Reading: cheaper than travel, richer than gold. 💛
- In love with every line of this masterclass. 📝
- Book hangover in progress. 📚💕
Mother’s Day captions for Instagram
- Behind every strong son is a mom who believed in him. 💪
- You make every day brighter, Mom. 🌟
- Forever grateful for your endless love. ❤️
- Maa—my heart’s first home. 🏡
- A mother’s love is pure magic. ✨
- Thanks for making the ordinary extraordinary. 💖
- To the woman who gave me not just birth, but everything. 🥰
- Home is where Mom is. ✨
- Sweetest hugs, warmest heart—that’s my mom. 🤗
- Love you to the moon and back, Maa. 🌙💕
Father’s Day captions for Instagram
- My first hero, and always will be. 💙
- Thanks for believing in me before anyone else did. 💫
- Who needs armor when you have Dad? ⚔️🛡️
- Forever my solid rock against storms. 🌪️
- Our family is built on your love, Dad. ❤️
- World’s #1 Dad award goes to Paa. ⭐
- Guiding hand, endless love. 🤝
- Cheers to the man who never backs down. 🥂
- Super strength, super smile—that’s my Dad! 👌
- You’re the reason I reach for the stars. ✨
Vacation/Holidays captions for Instagram
- Vacation mode 🔛😎✈️
- Sun, sand, and good vibes only. ☀️🏖️
- Escaping the ordinary one trip at a time. 🏝️
- Paradise found in ❄️🏞️
- Unplugged and unwinding. 📵
- Currently on cloud nine. ☁️
- Beach days are the best days, believe me. 🍹⛱️🌞 🌊
- Making memories all over the map. 🗺️🌎
- Wander often, wonder always. ✨📍
- Enjoying vacation, collecting seashells. 🐚
Social media holiday captions for Instagram
- Summer holiday magic is in the air. ✨
- Making memories, one holiday at a time. 🎁
- Cheers to spring and good vibes only. 🥂
- Cozy nights and festive lights. ❄️🌟
- Wrapped in love and holiday cheer. ❤️🎀
- ‘Tis the season to sparkle! ✨🎄
- Holiday vibes, warm hearts, full smiles. 🔔😊
- Snowflakes, hot cocoa, and cozy moments. ❄️☕
- May your holidays be merry and bright! 🎉✨
- Here’s to festive moments and joyful memories. 📸🎊
Contest & giveaway captions for Instagram
- 🎉 Want to win big? Follow, like, and tag a friend to enter! 🏆
- ✨ Giveaway time! Comment below with your favorite thing about [topic] to enter! 🔥
- 🎁 Ready for a surprise? Follow + Save + Tag to win our bundle! 💫
- 🌟 It’s GIVEAWAY season! Tell us your dream prize and tag two friends! 💭
- 📣 Who’s in? Follow & comment your answer for a chance to win! 🙌
- 💥 Don’t miss out! Like, share, and tag to enter this exclusive giveaway! 🎁
- 🌈 Season of giving is here, finally! Enter by tagging someone who needs this prize! 🏅
- 🎊 Win your favorite [product/experience]! Follow + Comment to join! ✨
- 🎀 The more tags, the higher your chances of winning! Good luck! 🍀
- 👉 Giveaway ends soon—get your entries in before time runs out! ⏳
Events/festivals captions for Instagram
Events and festivals are all about celebration, vibes, and memories. Whether you’re sharing pics from national holidays or seasonal moments with friends and family, choosing the right caption can make your Instagram post stand out and feel more festive!
4th of July captions for Instagram
- Stars, stripes, and summer nights | Happy Independence 🇺🇸 ✨
- Land of the free, because of the brave. 🇺🇸
- Fireworks and freedom—that’s the proud vibe! 🎆
- Red, white, and boom! 🎇
- Born to flash this 4th of July! ⚡
- Happy Birthday, America! 🎉 🇺🇸
- Home of born leaders, loving it. ❤️💙
- Grillin’ and chillin’ like true patriots. 🍔🇺🇸
- Current mood: cue the sparklers. 🎇
- Party like it’s the Fourth of July. 🥳 🇺🇸
Thanksgiving captions for Instagram
- Grateful, thankful, blessed. 🙏
- Eat, drink, and be thankful. 🍽️🦃
- Turkey, pie, and everything nice. 🥧🤲
- Thankful to GOD for today and every day. ❤️
- The perfect time to gather and give thanks. 🍁
- Happiness is homemade turkey. 🏡 🦃🍂
- Feeling grateful for every blessing. 🌟
- May your Thanksgiving be full of joy and turkey! 🍗
- Thankful hearts, full plates. 🧡🍽️
- Feast mode: ON! 🦃💛
Halloween captions for Instagram
- All treats, no tricks. 🍬 👻
- Happy #SpookySeason! 🎃
- Time to eat, drink, and be scary! 🕷️
- Witches just wanna have fun. 🧙♀️ 🎉
- Too cute to spook 👻💖
- Boo-yah! 🎃 👻
- Costume: Complete | Candy: Collected. 🍫 🎭
- Ghosting through October like… 👻 🍁
- Creepin’ it real. 🎃 😎
- Fright Night done right. 🌕 👻
Hanukkah captions for Instagram
- May your candles burn bright and your heart even brighter. 🕯️✨
- Latkes, lights, and love—Hanukkah vibes all around. 🥔🕎
- Eight nights of blessings, one season of joy. 💛🕯️
- Spin the dreidel and laugh with those you love. 🎲❤️
- You light up my life like the menorah lights. 🕎✨
- Here for the gelt and the glow. 🍫🕎
- Keep calm and dreidel on! 🎉🎲
- Wishing peace, joy, and eight nights full of light. ✨🌙
- Wishes as warm as the menorah’s flame. 🕯️💙
- Blessed with light, love, and laughter this Hanukkah. ✨🕎
Kwanzaa captions for Instagram
- Celebrating unity, creativity, and joy this Kwanzaa. ✨😊
- Umoja—together we rise. 🤝
- Harvesting hope and happiness this season. 🌾💙
- Celebrating heritage and bright futures. 🌟🛕
- From our family to yours—Happy Kwanzaa! 🕯️💚
- Embracing the Nguzo Saba—principles of strength. ✊🏽
- May unity and joy fill your heart this Kwanzaa. ❤️🖤💚
- Let the seven candles light your path ahead. 🕯️✨
- Celebrating culture, community, and connection at its peak. 🌍🤗
- Wishing you prosperity, peace, and pride. 🖤✨
Christmas captions for Instagram
- Merry & bright Christmas season! 🎄✨
- It’s beginning to look a lot like Christmas! ❄️🎁🎄
- Dear Santa, I’ve been good-ish. 😉🎄🎅
- Cozy nights and Christmas lights. Fa la la la la, la la la la! 🎶🎁
- Christmas magic is in the air. I can feel it in my veins! ✨❤️
- Meet me under the mistletoe. 💋🌿
- Sipping hot cocoa and spreading cheer this Christmas. ☕😃
- Let it snow, let it glow, let it go… ❄️🎅
- Merry everything and a happy always! 🎁🌟
- Catching snowflakes and holiday feels. ❄️❤️
Seasonal captions for Instagram
Seasons bring out distinct moods and visuals, from spring’s blossoms and summer’s sunshine to autumn’s cozy vibes and winter’s chill scenes. Seasonal captions help your photos feel more in sync with the specific time of year and pull your audience into the vibe you’re sharing.
Spring captions for Instagram
- Spring has sprung, and so have the flowers. 🌷
- Fresh blooms and fresh starts. 🌸 #SpringSeason
- Sunshine, flowers, and endless smiles. ☀️
- Blossoming into better days. 🌼
- Life begins with every spring bloom. 🌱
- Spring vibes and bright eyes. ✨🤩
- Warm breeze, cold coffee, happy me. ༄🥤
- Bloom where you’re planted. 🌺
- Spring—nature’s sweet way of saying “hello”. 🌞
- Petals and positivity everywhere. 🌷🤲
Winter captions for Instagram
- Winter vibes: covered in layers and wonder. ❄️🧥
- Snowflakes are winter’s confetti. ✨🎊
- Cuddle weather has officially arrived. 🧣🤗
- Frosty mornings and warm hearts. ☕❤️
- Winter magic everywhere I go. ❄️
- It’s a hot cocoa kind a day. ☕
- Snowy adventures and cozy memories. ⛄⛸️
- Winter skies and twinkling lights. The best view! ✨🤍
- Cold hands, warm soul. 💙🔥
- Blankets, snow, and cozy nights. Winter is officially here. 🌙🧤
Summer captions for Instagram
- Sun-kissed and summer-obsessed. ☀️
- Sunshine state of mind. 🌞
- Sunny vibes and tan lines. 🏖️
- Beach days and sun rays. The perfect combo! ☀️🏝️
- Stay salty, stay happy. 🌊🏊
- Endless summer moments. ✨🏖️
- Let the summer memories begin. ☀️✈️
- Sun, sand, and smiles. All I want from life. ☀️🤲😇
- Living life one summer day at a time. 👌
- Summer days = best days of my life. 🌞
Autumn/Fall captions for Instagram
- Fall in love with autumn colors. 🍁🍂
- Sweater weather and cozy feels. 🧣🍵
- Leaves are falling, and my heart is calling. 🍂🔥
- Pumpkin spice and everything nice. 🥰
- Autumn skies and golden vibes. 🍁💖
- Crisp air and cozy layers. 🧥
- Golden leaves and happy hearts. 💛
- Fall—nature’s second spring. 🌾😭
- Crunchy leaves and warm drinks. 🍁☕
- Cozy corners and warm memories. 🍂📖
Professional captions for Instagram
- Because professionalism never goes out of style. 💼✨
- Helping my business put its best foot forward. 👞📱
- From polished posts to powerful connections. Here we go! 📈✨
- Your brand’s personality, crafted with care. 💡🌟
- Human mind: Where clarity meets creativity. 🧠📊
- Trying our level best to make every post count. 📱🔥
- Precision, passion, and purpose—the goal of our every project. 📐💪
- Business as usual—but far better. 💼✨
- Focused on results, driven by values. 📈💡
- Let your work speak with confidence. 🔊💼
Read also: How to write a professional bio: best tips and tools
Captions for Instagram for business/promotional posts
- Limited time, unlimited opportunities—Shop Now! ⏳🛍️
- Your next favorite thing is just one click away! 🖱️✨
- Flash sale alert! Grab your favorites while they last! 💥🛒
- Savings that make you smile! Check out our latest deals! 😊✨
- From our hearts to your cart. Shop the love now! ❤️🛍️
- Don’t wait! Deals like this won’t last forever! 🔥💼
- New arrival, new obsession—link in bio! 🌟✨
- Your style just got an upgrade (explore now!) 💃💫
- Fresh vibes, fresh deals—start shopping! 🌈🛍️
- Shop smart, live stylish—Check out the latest catalog! 🛒💖
Captions for Instagram for soft launching/product launch
- Drumroll, please… our newest addition is finally here! 🥁✨
- Hot off the press! Say hello to your next obsession. 💖
- The wait is finally over—introducing [Product Name]! 🎉
- Fresh, fabulous, and available at outlets. Shop the new collection now! 🌟
- Big things come in new packages—meet our latest! 🎁
- Something special just dropped! Check the link in bio! 💫
- Today, we launch what we’ve been dreaming about since 2015! 🚀🙌
- Your wishlist just got an upgrade! Shop now for flat 50% off! 💎
- New drop, fresh feels—are you ready to explore? 🛍️
- Introducing innovation, specially designed for you. ✨🔍
Captions for Instagram for selling items
- Your perfect deal is waiting—add to cart today! 🛒✨
- Shop now and thank us later! 💖💳
- Hurry up, guys! Our best deals are running out! 🔥⏱️
- Fresh products, fair prices! Why wait? Place your order now! 🛍️🌟
- From our hands to your home—Shop with love. 🏡❤️
- Crafted with passion, delivered with supreme care. ✨📦
- Quality you can feel with your ❤️. Order yours today! 🛍️💫
- Every item here tells a story 📖. Get it now at 20% OFF. 🛍️
- Don’t scroll past—these deals are calling your name! 📱🔥
- Handpicked just for you! Grab yours before it’s gone! 💼✨
Captions for Instagram to get more followers
- Double-tap if you agree! ❤️
- Follow me & stay for the pleasant, +ve vibes. 🌟
- Tag 3 friends who’d love this post. 🙌
- Want more? Hit that follow button! 😉
- New here? Follow me & join the fam. 🚀
- Follow for daily inspiration drops. ✨
- Screenshot this & share with your crew. 📲
- Follow 👉 @yourusername for more cool posts! 😉
- Tag your travel buddy & plan the next adventure. ✈️
- Join the squad—follow and stay inspired. 💫
Captions for Instagram to get comments
- What’s your take on this? Comment below! 👇
- Which one’s your favorite | A or B? 💭
- Tell us your go-to snack in the comments! 😋
- Comment an emoji that sums up your mood! 💬
- Who else relates? Let me know! 🤔
- Drop your best advice for beginners! 💡
- Tag someone who needs to see this. 🏷️
- Share your biggest win this week! 🏆
- If you could describe today in one word, what would it be? 💬
- Comment 💯 if you’re here for football transfer window updates! 🔥
Captions for Instagram to drive traffic/generate engagement
- Save this for later so you don’t forget! 📌
- Tag someone who needs to see this. 👀
- Double-tap if this made you smile hard! 😂
- Share this in your story if you agree! 🔁
- Tell me your biggest goal right now! 🎯
- Want more tips on this? Save this post! 🧠
- Swipe right to see the magic unfold! ➡️
- Let’s get the conversation going—comment below! 💬
- Drop an emoji if you’re feeling 🌈 today!
- DM me your questions—let’s chat! 💌
Brand partnership captions for Instagram
- When great minds come together, magic happens. 🧠✨
- Two brands, one vision! Big things ahead. 🚀
- Collaboration at its finest. Together, we’re unstoppable. 💥💪
- Thrilled to partner with @partner — stay tuned! 🤝
- Bringing innovation to new heights together! 🌟
- Teaming up to bring you something special. Stay tuned! 💫🔜
- Strength in unity—exciting things are on way! 🎉🙌
- Together we’re creating waves—watch this space! 🌊
- Proud to collaborate with @partner on this remarkable journey! 💖🤜🤛
- Uniting visions to inspire and empower you! ✨💡
Employee appreciation captions for Instagram
- Behind every success is a team that never quits! Thank you, guys. 💼❤️
- Big shout-out to our amazing team—you make magic happen every day! ✨💫
- We appreciate every idea, effort, and smile you bring to the workplace. 👏
- Meet the people who make the impossible look easy. 🌟🚀
- Our team is the heart of our brand ❤️. Grateful for each one of you. 🙌
- [Employee name]’s dedication drives our success. Thank you! 🏆💯📈
- Celebrating the stars who make great things happen. ⭐👏🥇
- To our team: Your passion is our ultimate strength. 💪
- Recognizing the excellence that keeps us moving forward. 📈
- We couldn’t do it without you! Here’s to our work family! ❤️👏
Celebrating a milestone captions for Instagram
- We did it! Thank you for being part of this journey. 🎉❤️
- Another milestone unlocked, and it’s all because of you! 🙏🙌
- Cheers to growth, community, and new beginnings! 🥂
- Milestone moment! Your support and endless effort made this possible! 🌟🎯
- Celebrating success and the people who helped us get here. ❤️👏🏆
- Every step forward feels sweeter with you along for the ride! 🚀🔥
- Hitting [milestone number] and feeling grateful! 📈🤲
- From day one to today—thank you for believing in us! 💫❤️
- Achieved another goal 💯. On to the next 💪.
- This moment belongs to you as much as it belongs to us. 🤝🌍
Podcast promotion captions for Instagram
- 🎙️ New episode alert! Tap the link in bio to listen now.
- This Friday night on the mic, we step into [topic]. Don’t miss it! 🔥
- 👂 Hear what [guest name] had to say. New episode out now!
- Ready for some inspiration? Episode [number] just dropped! ▶️
- 📅 Set a reminder—our latest podcast is live!
- We’re talking about all things on [topic]. Tune in via the link in bio! 🎧
- 💬 Join the conversation! New episode available now! 👇
- Behind the scenes and real talk. Episode out today at 11 pm! 🎤
- Catch up on past episodes while you wait—link in bio! 📲
- Your weekly dose of insights just arrived—press play! ▶️
Blog promotion captions for Instagram
- ✍️ New blog post live! Discover our take on [topic]. Link in bio!
- Want more on this? The full blog is waiting, click the link! 🔗
- Just published: deep dive into [topic]. Check it out! 📚
- Find out the secrets behind [topic] — new blog up now! 💡
- 📝 Ready for insight? Our latest blog has all the deets. Link in bio!
- Get smarter on [topic] with our newest post! 🔍
- Thoughtful, helpful, and just published! Go & read it! 📲
- Swipe up to read the full blog on [topic]! (or check the link in bio) 🚀
- Your next read is here! Head to the blog now! 📖
- Blog alert! 💥 We’re unpacking [topic] so you don’t have to. 🙌
Captions for Instagram story
Instagram Stories are perfect for quick, eye-catching moments you want to share with your followers in real time. No matter if it’s you and your friends, a beautiful sunset, your gym grind, a birthday countdown, or your dog being adorable, a short, fun caption helps keep your IG stories engaging and relatable.
Captions for Instagram story with friends
- Forever my ride-or-die crew 🤝
- Friends make everything special 🌟
- Adventures double the fun 🏞️
- Sweet times with sweeter friends 🍩
- Besties 💛 + Good vibes only ✨
- Beach days with friends are the best days 🏖️
- Sunsets are better with friends by your side 🌅
- Cheers to us! 🥂
- Friends like family 💕
- Laughs that never end 😄
Sunset captions for Instagram story
- Chasing sunsets and dreams 🌅✨
- Every sunset brings a new promise 🌞
- Golden hour glow up ✨🌇
- Painting the sky with color 🎨
- Sunset state of mind 🌇
- Aesthetic memories at dusk 🌅💕
- End the day on a beautiful sunny note 🌞
- Sunset kisses and evening bliss 🌇💋
- Peace, love, and sunset vibes 🌞💖
- Watching the world light up at dusk, the best feeling ever 🌅👌
Gym captions for Instagram story
- Sweat today, shine tomorrow 💦
- Beast mode: ON 🔥😈
- One more rep, one step closer 💪
- Gym hair, don’t care 😉
- Train like a beast 🏋️♂️
- Discipline = Ultimate freedom 🔥
- Today’s workout = energy boost 💥
- Push harder than yesterday 💪
- Fitness is my therapy 🎧🔋⚡
- Strong mind, stronger body 🧠💪
Birthday countdown captions for Instagram story
- Birthday countdown: [X] days to go! 🎉⏳
- Can’t wait to celebrate! 🎈🥳
- Almost my fave day of the year! ✨🤗
- Day [X]: Birthday mood loading… 🍰🍾
- Bring on the cake 🎂! 10 minutes left ⏱️!
- Countdown: Let the celebrations begin! 🥳🙌
- 7️⃣ days until I level up! 💫
- Growing older, feeling awesome! 🌟😎
- Just a few more sleeps till my day! 😴
- Birthday glow loading… ✨🔜
Dog captions for Instagram story
- My furry best friend 🐶💕
- Tail wags, happy hearts 🐾
- Adventure buddy on four paws 🐕
- Daily walks, endless love 🚶♂️🐾
- Paw prints on my soul 🐾❤️
- Best co-pilot ever 🚗🐶
- Fetch goals mastered 🎾
- Furry cuddles all day 🛋️💞
- Sunny days & puppy play ☀️🐕👌
- Home is where my pup is 🏡🐾
Also read: 400+ best Instagram bio examples to stand out in 2026
Amazing benefits of engaging Instagram captions
Great Instagram captions do a lot more than just label your photo. They help you connect with your audience, strengthen your presence on the platform, and even get more eyes on your content, making your posts way more effective overall.
Boosts engagement
When you write captions that ask questions or invite interaction, followers are more likely to like, comment, share, or save your post. This informs the Instagram platform that your content is worth showing to more people.
Increases discoverability
Captions that use relevant keywords and hashtags help Instagram understand what your content is about, so your posts can show up in search results and reach users who don’t already follow you, seamlessly.
Adds context & depth
A caption gives your audience the “why” behind the image. It explains what’s happening, sharing thoughts, or telling a story, so your visuals feel more meaningful and less random.
Builds brand personality & trust
A consistent voice in your captions helps shape how followers perceive you or your brand. Being authentic and relatable uplifts trust and makes people feel more connected to your content.
Drives action (CTAs)
Including a clear call to action, such as “tap the link in bio,” “comment your thoughts,” or “save this post,” gives people direction and increases the chances they’ll take the next step you want them to take.
Improves accessibility
Good captions can describe what’s in the image or what you’re sharing, making your content easier to understand for people using screen readers or those who can’t see the picture clearly.
Enhances SEO
Instagram now uses caption text and hashtags in its search algorithms, so well-written captions with keywords can help your posts surface in Instagram search and hashtag feeds, boosting visibility.
Increases time spent on post
Longer, thoughtful captions can encourage followers to pause and read, which signals to the Instagram algorithm that your content is valuable. This can help your post get shown to more people!
Tips for selecting the right captions for your Instagram posts in 2026
Choosing the right caption can make your posts feel more meaningful, relatable, and effective; not just pretty words under a photo.
The best captions match your audience, add real value, and guide your followers to interact with your content.

Tip #01: Know your audience & brand voice
Before you type a word, think about who you’re talking to and how you want to sound. A caption that feels too formal for a fun audience (or too casual for a professional one) won’t click.
Tailor your language, slang, and tone to fit your followers, and keep your voice consistent so people recognize your style instantly.
Tip #02: Provide value & tell stories
People engage most with captions that give them something (a helpful tip, a quick story, or a moment that makes them feel something).
Sharing a relatable anecdote around your photo or giving valuable insights makes your content more memorable and encourages people to linger, react, or comment.
Tip #03: Mind the length & formatting
There’s no one perfect length, but you should match your caption to its purpose.
Short, punchy lines work well for quick posts, while more extended captions are great for stories or more in-depth messages.
Note: Use line breaks, spaces, and emojis to make long captions easier to read on small screens.
Tip #04: Stay true to yourself
Authenticity still matters more than polished marketing speak. When you write like you’re talking to a friend (honestly and clearly), people connect better with your content.
Avoid jargon or trying to sound “too perfect,” because genuine captions tend to build real engagement and trust.
Tip #05: A clear call to action (CTA)
A great caption doesn’t just sit there; it guides your audience. Whether you want them to comment, save, click your link, or share your post, tell them what you want them to do in a friendly way.
Simple prompts like “Tap the link in bio” or “Comment your thoughts below!” enhance interaction and make your posts more purposeful.
Tips for crafting unforgettable & winning Instagram captions
The best captions don’t just support your photo; they amplify your message, grab attention, and boost engagement exceptionally. With the proper structure and strategy, your words can make your posts more effective and memorable.

Tip #01: Hook the audience immediately
The first line of your caption needs to stop the scroll and pique interest right away. Think of it like a headline that makes people want to read more.
Note: Using a bold statement, question, or curiosity-sparking phrase in the first few words can significantly increase engagement.
Tip #02: Share experiences & emotions
People connect with real feelings and experiences. No matter if it’s a fun moment, a challenge you’ve overcome, or an inspiring insight, sharing something personal or relatable helps build a deeper connection with your audience.
Tip #03: Format for readability
Break lengthy captions into short lines or paragraphs and use spacing or emojis to make the text easier on the eyes. This improves readability on mobile screens and encourages people to actually read your message.
Tip #04: Use relevant hashtags strategically
Hashtags help your post reach a wider audience beyond your followers. Choose a mix of popular and niche hashtags that fit your content.
Note: Putting hashtags at the end or in the first comment keeps your caption clean while boosting discoverability.
Tip #05: Maintain a consistent brand voice
Whether you’re playful, inspiring, or professional, sticking to a consistent tone helps your audience recognize and relate to you. Over time, this builds familiarity and trust, so your captions feel like they’re part of a cohesive story.
Use Replug’s Instagram caption generator for generating the best IG captions in seconds!
Struggling to come up with fresh, engaging captions every time you post?
Replug’s Instagram caption generator takes the pressure off by giving you ready-to-use caption ideas in just a few clicks, so you can focus more on sharing great content and less on staring at a blank screen.
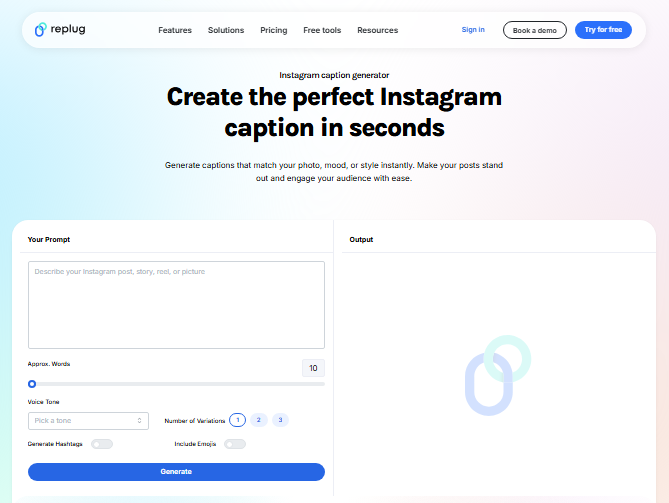
Here’s how it works, step-by-step:
1. Enter your prompt: Start by typing a brief description of your post or what you want your caption to be about. This helps the tool understand the tone and message you’re aiming for.
2. Tailor the word count: Decide whether you want a short caption or something longer with more detail, and set the word count accordingly.
3. Pick your tone: Choose the tone that fits your brand or post style. It could be joyful, professional, formal, informal, etc.
4. Add emojis & hashtags (optional): Toggle the emoji and hashtag options on or off depending on whether you want your caption to include mood cues or boost reach.
5. Choose how many variations: Select the number of caption suggestions you want. This gives you options to pick the best fit. (3 variations are available)
6. Click “Generate”: Hit the Generate button and watch the tool create multiple caption ideas instantly that you can copy and paste into your Instagram post, hassle-free!
Replug’s caption generator not only helps you come up with captions fast, but also keeps your voice consistent and creative, making your Instagram posts more engaging without the usual caption-writing stress.
Wrapping up
Coming up with the perfect Instagram caption isn’t just about cute phrases anymore! It’s about connecting with your audience, telling your story, and boosting engagement in real, measurable ways.
From understanding your audience and formatting your text right to using tools that speed up your workflow, good captions play a massive role in helping your IG posts perform better in 2026.
And when it comes to streamlining your social media efforts overall, giving Replug.io a try can make a real difference.
Replug is an all-in-one link management platform that lets you build custom bio links, where you can connect all your content, products, and offers in one place. This is so that your followers always find exactly what you want them to see.
Check it out and turn your Instagram bio into a powerful traffic and conversion hub!
Frequently asked questions
What is the best Instagram caption?
The best Instagram caption depends on your post and audience, but generally it’s one that feels real, adds meaning to your photo, and invites interaction.
It should match your tone (funny, heartfelt, or informative), and often include a question or call to action to spark engagement. Successful captions balance personality with clarity, so people connect with what you’re sharing.
What are small captions?
Small captions are short, concise text lines that usually stay well under the character limit and get to the point quickly. These work great for quotes, one-liners, or when the photo speaks for itself, especially since Instagram shows only the first ~125 characters before users click “more.”
What is a good photo caption?
A good photo caption explains or enhances what the viewer sees, whether by adding context, emotion, or a relevant story. It might include a little background, a fun fact, or a question that makes your audience pause and relate to the image more meaningfully.
How do I caption a self-pic?
For a self-pic, keep your caption authentic and personal. You can comment on how you’re feeling, share a confident thought, or add a playful line about the moment. Adding a slight touch of humor or honesty often makes selfies feel more relatable.
What is the Instagram caption character limit?
Instagram allows captions up to 2,200 characters, including spaces, emojis, and hashtags. However, only the first ~125 characters are shown before the text is cut off with “more,” so make your opening words count.
How do I make my Instagram captions more engaging and interesting?
To make captions more engaging:
– Start with a hook,
– Share a short story or emotion,
– Include a clear call to action (like asking a question), and
– Use emojis or line breaks for readability.
Keeping your voice real and approachable helps your audience connect and respond.
Should I use hashtags in my Instagram captions or not?
Definitely! Hashtags can help categorize your content and make it discoverable when people search for topics, but they’re no longer a magic growth hack on their own.
Using a few relevant, specific hashtags (about 3–8) that match your post content is better than stuffing random ones. Instagram’s algorithm now prioritizes engagement and caption content, so keep hashtags meaningful and minimal.
How do I create Instagram captions that align with my personality or brand image?
To match your personality or brand, maintain a consistent tone across all posts. Write captions the way you speak (e.g., casual, witty, or professional), and use recurring phrases that reflect your style. Always align your captions with your values and audience expectations to make your voice feel authentic.
Do short captions work better than long ones on Instagram?
Both can work; the key is relevance and clarity. Short captions are great for quick messages or attention hooks, while longer ones help tell a story or share more profound thoughts.
Instagram’s algorithm doesn’t penalize extended captions, so choose length based on your content and audience preference, not a fixed rule.
Why do you need a game-changing or classy caption for your Instagram post in 2026?
A strong caption grabs attention in a crowded feed, adds meaning to your visuals, and encourages interaction, such as likes or comments. In 2026, with more video and AI-driven discovery, captions that connect emotionally or inform help your posts stand out and build stronger audience relationships.
When is the right time to post on Instagram?
There’s no one perfect time for every account, but general trends show strong engagement mid-week and mid-day (especially Tuesday–Thursday between 9 AM–3 PM local time), since many users scroll then.
The best time for your audience may vary, so check your Instagram Insights to see when your followers are most active.
![1000+ best captions for Instagram posts & stories in 2026 [Copy & Paste]](https://internal-blog.replug.io/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/1000-best-captions-for-Instagram-posts-stories-in-2026-Copy-Paste.png)